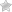When grocery shopping, you're likely very familiar with bananas. But have you ever been stumped when you've come across a banana look-alike? If you think you've been duped, think again. You're likely looking at plantains.
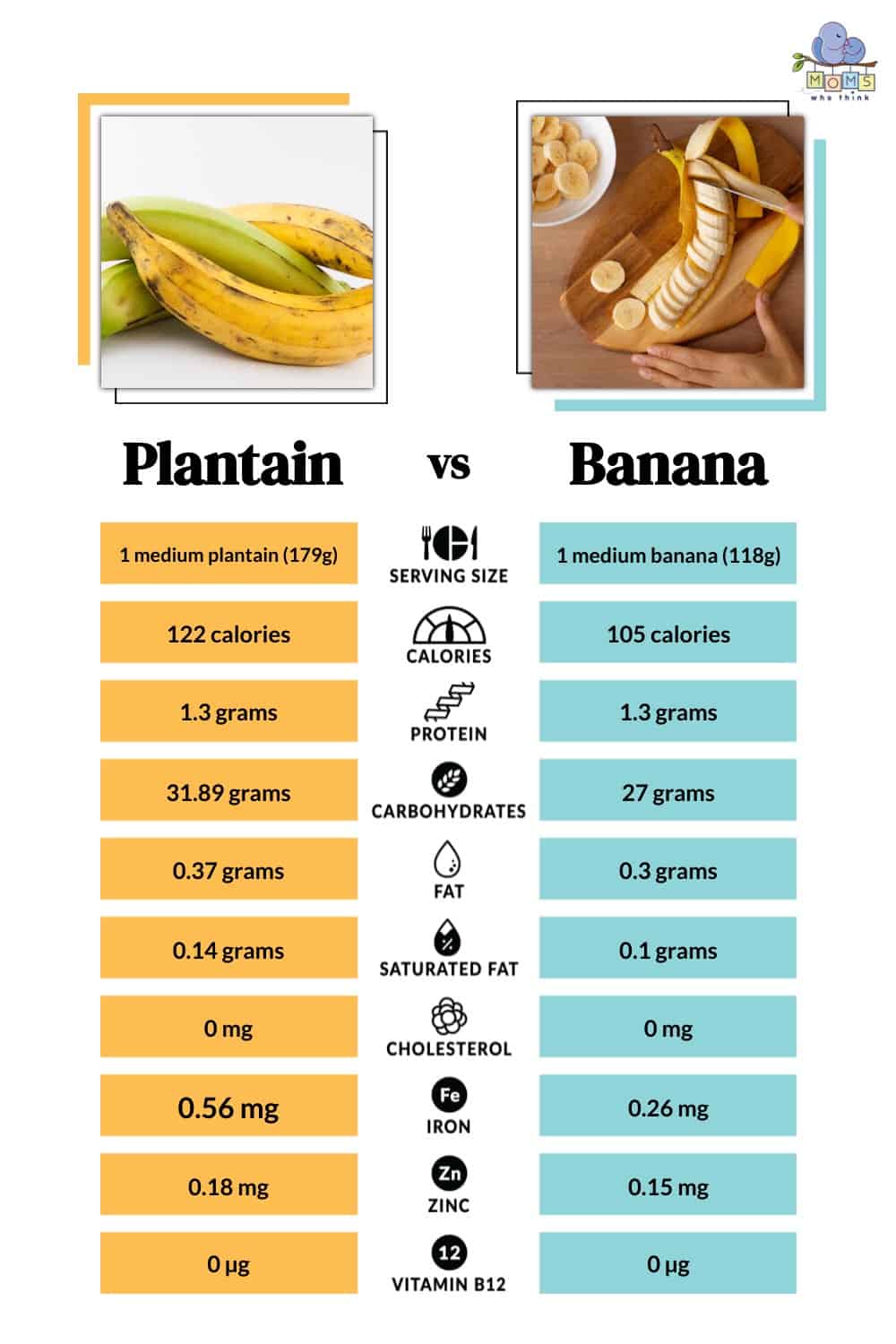
While plantains and bananas come from the same family and look incredibly similar, these fruits are not the same. Plantains can be eaten ripe or unripe and are often more savory tasting, especially if they aren't ripe yet. On the other hand, bananas are typically only eaten when ripe and have a much sweeter taste than their look-alike.
From the way they're cooked to the way they taste and are grown, plantains and bananas have many differences. Let's take a closer look at what sets these two fruits apart.
What are Plantains?

©Anamaria Mejia/Shutterstock.com
While plantains look similar to bananas, they often have a tougher peel and are larger in size. They're also starchier than bananas, so plantains typically have to be cooked before being consumed, unlike bananas which can be eaten raw. Plantains can also range in color from green to yellow to brown, depending on ripeness. As they ripen, they tend to get sweeter in taste.
Plantains are typically grown in Southeast Asia, Central Africa, the Caribbean, and other tropical regions. This makes them a popular item in African, Caribbean, and Latin cuisines. The fruit is sometimes cooked like a vegetable due to its starchy, less sweet flavor.
What are Bananas?
You're probably well aware of bananas as they're a staple produce item in most local grocery stores. This fruit (along with plantains) is part of the Musa family of plants. According to Healthline, bananas are a good source of fiber, potassium, and vitamins B6 and C. They are much sweeter than plantains, as ripe bananas have a higher amount of sugar from carbs. This sweetness makes bananas a popular choice to include in desserts.
Bananas are primarily grown in Southeast Asia, including India and China, but they're also grown in numerous other countries around the world. Their wide availability makes them a more popular product than plantains.
Plantain vs. Banana: What are the Differences?
As mentioned, plantains and bananas differ in taste and size. Bananas tend to be sweeter and are easy to find in the produce section of your grocery store. Plantains, on the other hand, are starchier, have thicker skin, and are often cooked before eating due to their heavy starchness.
Here's an in-depth look at the four key differences between plantains and bananas.
Origin
Both plantains and bananas are grown in bunches from trees and grow best in countries that have humid and tropical climates. Additionally, both fruits are native and naturally grown, not man-made. However, they each have their own story in the role they play as a food source.
According to Britannica, plantains originated in Southeast Asia. As trade routes began moving to Africa and the Caribbean, the plantain traveled to new countries. This fruit is now one of the most popular produce items and exports in Latin America as it grows best in hot and humid climates.
Bananas have a much longer history, with scientists believing this fruit dates back thousands of years. Science.org reports that the first traces of bananas can be found in Papua New Guinea. The first bananas were filled with black seeds and were difficult to eat. As they've changed and become more “domesticated,” the seeds have reduced significantly in size, providing an edible fleshy fruit inside the peel. Today, bananas are highly popular and grown in different countries worldwide, primarily in India and China.
Appearance
This is an area where plantains and bananas are closely similar, as it's easy to mistake one for the other at quick glance. However, these two fruits do differ. Once you understand the characteristics of both of these fruits, you'll be able to tell one from the other the next time you grocery shop.
Plantains are often larger than bananas and have a thicker peel. This fruit is also often eaten before its ripe, which means a group of plantains may look very green at the store. Bananas, on the other hand, are smaller than plantains and are often eaten ripe. This means you'll want to purchase bananas that look yellow or at least have less green than yellow.
Taste and Texture
If you happen to mistake a plantain for a banana, you'll quickly notice the difference after you take a bite.
Plantains are firm and have a mild, starchier taste than bananas. When they're unripe and green, they tend to be the most starchy. When they're allowed to ripen, they can become sweeter, but they're still not as sweet as bananas.
So, we can see that bananas are sweet. And the longer they're allowed to ripen, the sweeter they become. Bananas are also soft and creamy on the inside, much different than the firmness of plantains.
Cooking Methods

©Lekan Agboola/Shutterstock.com
When used for cooking, plantains are often treated as more of a vegetable than a fruit due to their higher level of starchiness. They can be cooked when ripe or unripe, which allows them to be used in both sweet and savory dishes. However, they're most commonly used as a savory side dish. Plantains are relatively versatile as they can be baked, fried, or sauteed. They're popular in Caribbean, African, and South American cuisines.
Because of bananas' sweetness, they're used quite differently in cooking. This fruit can be eaten raw but is also popular in desserts and baked goods. Ripe or overripe bananas are often smashed and pureed before being added to banana bread, pancakes, and muffins. Slightly underripe or ripened bananas can be sliced and eaten on oatmeal or as a snack. If your bananas are becoming ripe before you can use them, you can also place them in the freezer to use in banana bread or other recipes later.
Plantain vs. Banana: Nutritional Value
The nutritional value between plantains and bananas is fairly similar. However, plantains' starchiness leads to a higher level of carbs and calories. While bananas have fewer carbs than plantains, those carbohydrates usually come from sugar. Both offer healthy fiber, potassium, and vitamin B6, however.
Can you Substitute a Plantain for a Banana and Vice Versa?
While it depends on the recipe, plantains and bananas have enough of a difference in taste and texture that they're not ideal substitutes for each other.
Plantains are milder, starchier, and firmer than bananas, so using a banana instead of a plantain would add a lot of sweetness that might not fit well in your recipe. Other replacements for plantains you can try in a pinch include yucca root, potatoes, yams, and sweet potatoes. Just keep in mind that these substitutes may not have the exact same taste or texture as plantains, which could alter your recipe.
Due to the sweetness and softer texture of bananas, plantains may be too firm and starchy to be a good replacement. Other substitutes for this fruit include applesauce, avocado, mashed sweet potato, or even canned pumpkin, as these items provide the same consistency as a mashed banana for baking.
If you absolutely must substitute a banana with a plantain or vice versa, determine what ripeness your replacement needs. Green and underripe bananas will work as a better replacement for plantains, while overripe plantains will add more sweetness as a better substitute for bananas.
Final Thoughts
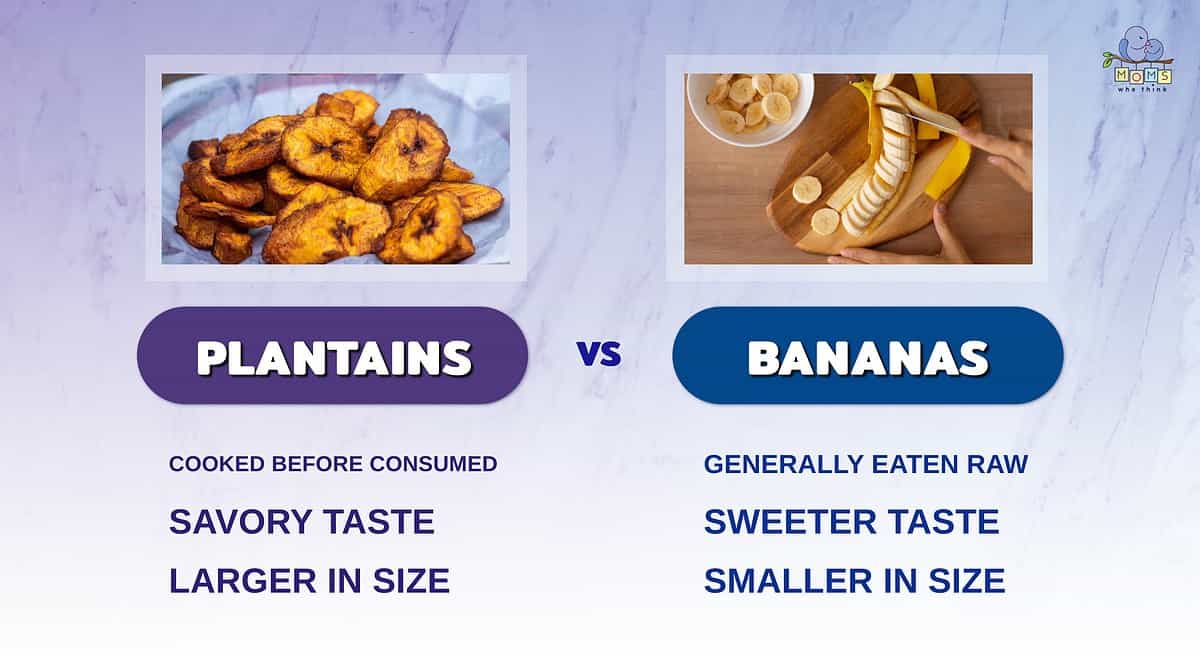
While it's not uncommon to get the two confused, plantains and bananas are actually quite different. Let's take a look at a few of the more common distinctions:
- Plantains have thicker skin, while bananas are softer and have a thinner peel.
- The biggest difference is the taste. Plantains are starchier, while bananas have a sweeter taste, particularly when they're more ripe.
- Bananas are generally eaten raw or baked in bread and pancakes. On the other hand, plantains are usually fried or used in savory dishes.
While plantains and bananas have a lot of similarities and look almost identical, these two fruits are not the same. Plantains are larger, starchier, and used in savory dishes, while bananas are smaller, sweeter, and used in desserts and baked goods. Keeping these differences in mind will help you determine which one is best for your next recipe.
Banana Recipes
Print
Banana Bread
Ingredients
1 cup butter, softened
2 cups sugar
7 large over-ripe bananas, mashed*
1 1/2 teaspoons vanilla extract
4 eggs, slightly beaten
3 cups flour
1/2 teaspoon salt
2 teaspoons baking soda
Instructions
1. Cream the butter and sugar. Blend in the bananas, vanilla and eggs.
2. Whisk together the dry ingredients.
3. Add to the bread mixture and mix until just combined. Pour into two greased 9×5 inch loaf pans.
4. Bake at 350F. Check on the bread after 35 minutes (it may take up to 60 minutes). Banana bread is done when a toothpick inserted in the middle comes out clean. Cool the banana bread in the pan for 10 minutes then cool completely on a wire rack.
Notes
*If your bananas aren't ripe enough, you can quick-ripen them in the oven. Peel and bake at 450°F on an ungreased baking sheet for 10 to 15 minutes until very soft.
Remember, for the best flavor use bananas that have skins that are almost black. Using bananas that aren't over-ripe will not produce the full banana flavor that good banana bread has, and the texture will also be different.