While both are considered butter and bring delicious flavor to just about any meal, there are key differences between clarified butter vs. ghee. For example, both are heated butter with the milk solids removed. However, ghee is a version of clarified butter with extra heat so it is browned and has a strong, nutty, rich taste. But which is healthier? Are there any other differences you need to know?
Clarified Butter vs. Ghee: Key Differences
There are distinct differences between clarified butter and ghee.
Flavor and Aroma
Clarified butter has a mild, buttery flavor with an enticing aroma
Ghee has a rich, nutty and almost caramelized type of flavor. It has a stronger aroma compared to butter.

©vm2002/Shutterstock.com
Shelf Life
Clarified butter has a shorter shelf life compared to ghee. It can last up to six months in an airtight container. And since its water and milk solids have been removed, it needs to be stored properly. This means it is important not to let any water get in the container. If so, the clarified butter will start to spoil and go bad. Refrigeration will help to extend its shelf life and flavor.
Ghee on the hand, has a longer shelf life than clarified butter. This may be surprising especially since ghee is made from clarified butter. So why the longer shelf life? It is because of the extended cooking process of ghee. During this process, more moisture and milk solids are removed. That’s why ghee can be stored at room temperature for longer periods without the threat of spoiling or going bad.
Clarified Butter vs. Ghee: How to Use Them
You can use both clarified butter and ghee interchangeably. However, here are some ideas you may find helpful when considering using clarified butter or ghee:
Clarified Butter
This butter is widely used in sauteing, shallow frying and as a cooking fat. And because of clarified butter’s neutral buttery flavor it finds its way in a variety of dishes! Many people enjoy clarified butter as a substitute for regular butter. For example, you can use clarified butter as a dip to cooked seafood like lobster, crab or shrimp, sauces and even as tasty buttery popcorn for movie night!
Ghee
You will find ghee to be a precious and savory staple in Indian and Middle Eastern recipes. It has a high smoke point of 485°F which is the temperature fats become volatile and start to smoke. This makes it a stable and safe cooking oil. And it adds a distinctive flavor by shallow frying, deep-frying, sauteing, and even in many sweet dishes. Some examples include using ghee as a cooking oil, drizzling it over baked goods, popcorn or meats, for sauces, roti and drinks.
It is very common in Indian cuisines. However, it is more predominantly found in South Indian cuisines. For instance, ghee enhances the flavors of curries and makes for savory and tasty rice dishes and desserts. A cherished tradition in South India involves drizzling ghee over rice, creating a delightful combination when paired with pickles and curries. As avid enthusiasts of ghee, South Indians rank among its most fervent consumers.

©Heike Rau/Shutterstock.com
You can even use it as a natural way to nourish your skin and hair as is done in Ayurveda!
Clarified Butter vs. Ghee: Nutritional Value
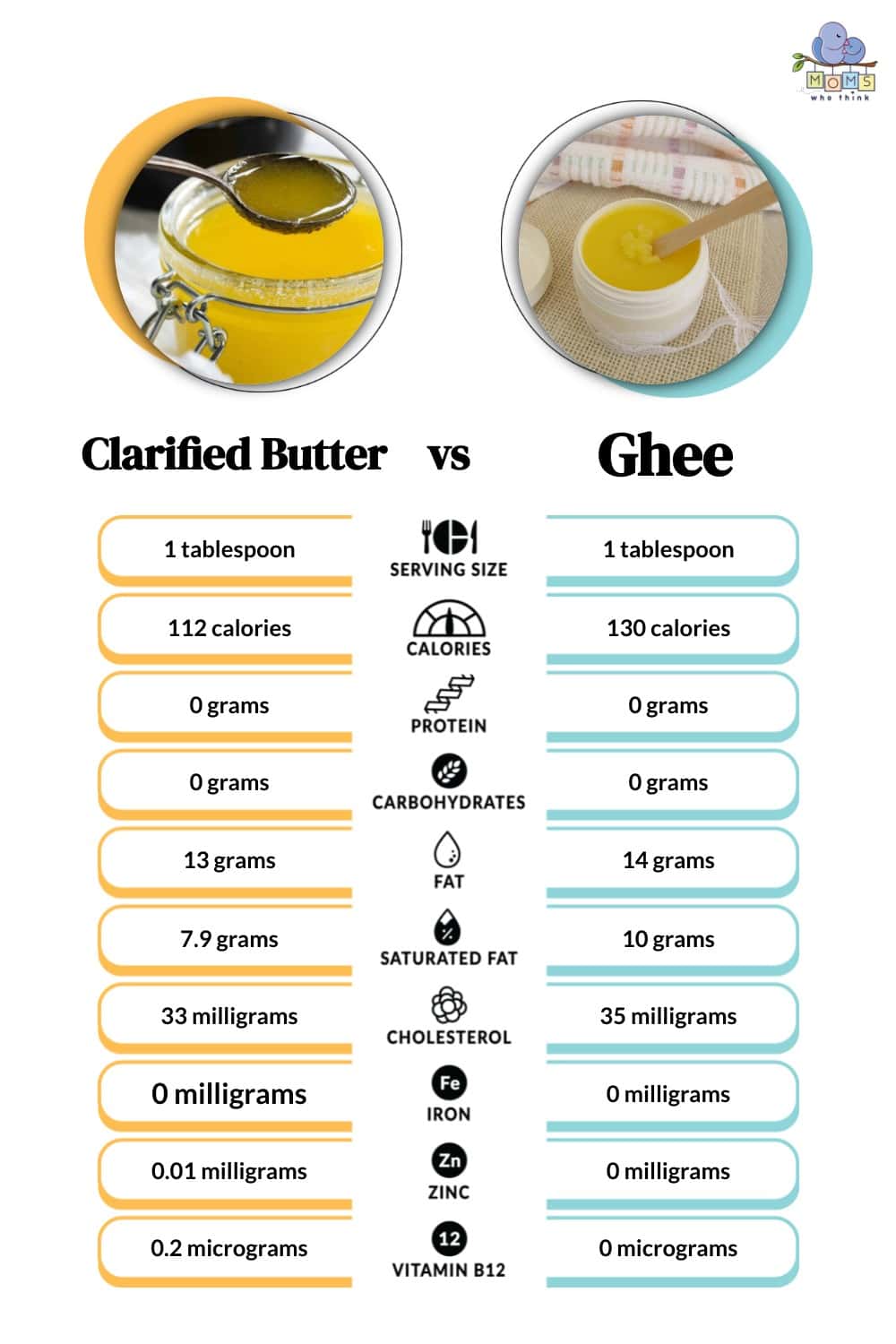
What is Clarified Butter?
It’s like savory liquid gold! Clarified butter is the type of butter that has had the water and milk solids removed, leaving behind only the pure, clear, and golden-yellow liquid butterfat.
Clarified butter is also known as drawn butter, which is another term for melted butter. And that’s exactly what happens. Simply put, it is just regular unsalted butter that through heat slowly melts and then it is the process of separating it into the three main components: butterfat, water, and milk solids.
The resulting product is clarified butter, which has a higher smoke point compared to regular butter and is often used in cooking and frying because it does not burn as easily. It has a mild, buttery flavor and is free of the water and milk solids that can make regular butter prone to burning and spoiling at high temperatures. Clarified butter is a versatile cooking fat used in various cuisines around the world.
What is Ghee?
This is a type of clarified butter that comes from India. It is cooked longer than clarified butter giving it a richer, nuttier flavor, has a longer shelf life and is able to handle high heat. Ghee is made up of the fat from unsalted butter and approximately 62% of it being saturated fats. It contains small levels of lactose and casein which means most people who are lactose intolerant or have milk allergies, are able to use it without being a problem.
Clarified Butter vs. Ghee: How to Make at Home
If you were to buy clarified butter or ghee at the store you may notice prices vary. And sometimes they can be pretty steep. However, you can make both clarified butter and ghee at home by following a very simple recipe. It takes about 30 minutes. For example, to make 2 cups of clarified butter or ghee, here’s what you need to do:
Ingredients:
1 pound of regular unsalted butter
Directions:
1. Take a pound of unsalted butter and cut it into small pieces.
2. Put the butter in a small saucepan and heat it over medium-high heat until it starts to simmer and foam appears on the surface.
3. Stir the butter and lower the heat to medium-low. As you do this, the foam will gradually disappear, and you'll see the solid bits (milk solids) sinking to the bottom of the pan.
4. If you want clarified butter, you can stop here. But if you want to make ghee, keep cooking it on low heat for about 20 minutes until the milk solids turn light brown.
5. Remove the saucepan from the heat and let it cool for 10 minutes.
6. Strain the liquid through a cheesecloth-lined strainer into a jar. This liquid is your homemade ghee.
That's it! You've made ghee from butter.
Clarified Butter vs. Ghee: Health Benefits
While both clarified butter and ghee offer health benefits, there are some important things to consider. First let’s look into the health benefits.
These can aid in supporting digestive health because they contain butyric acid. This type of acid helps lower inflammation levels. Both are rich in key nutrients like vitamin A, E, and K. So they support eye and skin health and help boost your immune system. They also help promote a healthy heart and fight inflammation.

©Tati Liberta/Shutterstock.com
Important Health Concerns
Now that you understand the health benefits of clarified butter and ghee, this doesn’t mean you should use slabs of them as a substitute for butter or even add dollops in your morning cup of Joe. Why? Because it’s still a saturated fat. And eating too much saturated fat can cause a blockage of arteries and increase your risk of heart disease and stroke.
And as the saying goes “too much of anything isn’t good”. So, for example, while there are studies such as the International Quarterly Journal of Research in Ayurveda that show ghee supports healthy HDL (good) cholesterol levels, you still need to take precautions. This is especially true if you struggle with LDL (bad) cholesterol levels then you may want to limit your daily serving of ghee to no more than 1 tablespoon per day.
That’s why moderation is the key even though these have key vitamins. Lisa Sasson, clinical professor in the department of nutrition and food studies at New York University says, “you’d have to eat so much ghee to get a significant amount.”
Final Thoughts
All in all, the choice between clarified butter vs. ghee boils down to how you will use them. Both are types of butter with the water and milk solids removed. Clarified butter is clear and neutral in flavor, while ghee, also known as “liquid gold” has a rich, nutty taste, and a longer shelf life. They're good for lactose-intolerant individuals and used in cooking, especially in Indian and Middle Eastern dishes. However, please keep in mind this: Like all fats, they should be used in moderation as part of a balanced diet.

