Aren’t both of them pretty much the same? No. And the differences may surprise you. While both are natural sugars, the biggest difference is erythritol is an artificial sweetener made from corn using a fermentation process. On the other hand, Stevia is a natural sweetener that comes from the stevia plant. Erythritol is not as sweet as stevia which makes it easier to use.
In this article, you’ll discover key differences between erythritol vs. stevia. And you can decide which is the better choice for flavor, nutrition, and guilt-free indulgence for you and your family.
Erythritol vs. Stevia: Key Differences
The main key differences between are two things: origin and taste.

©Tatiana Frank/Shutterstock.com
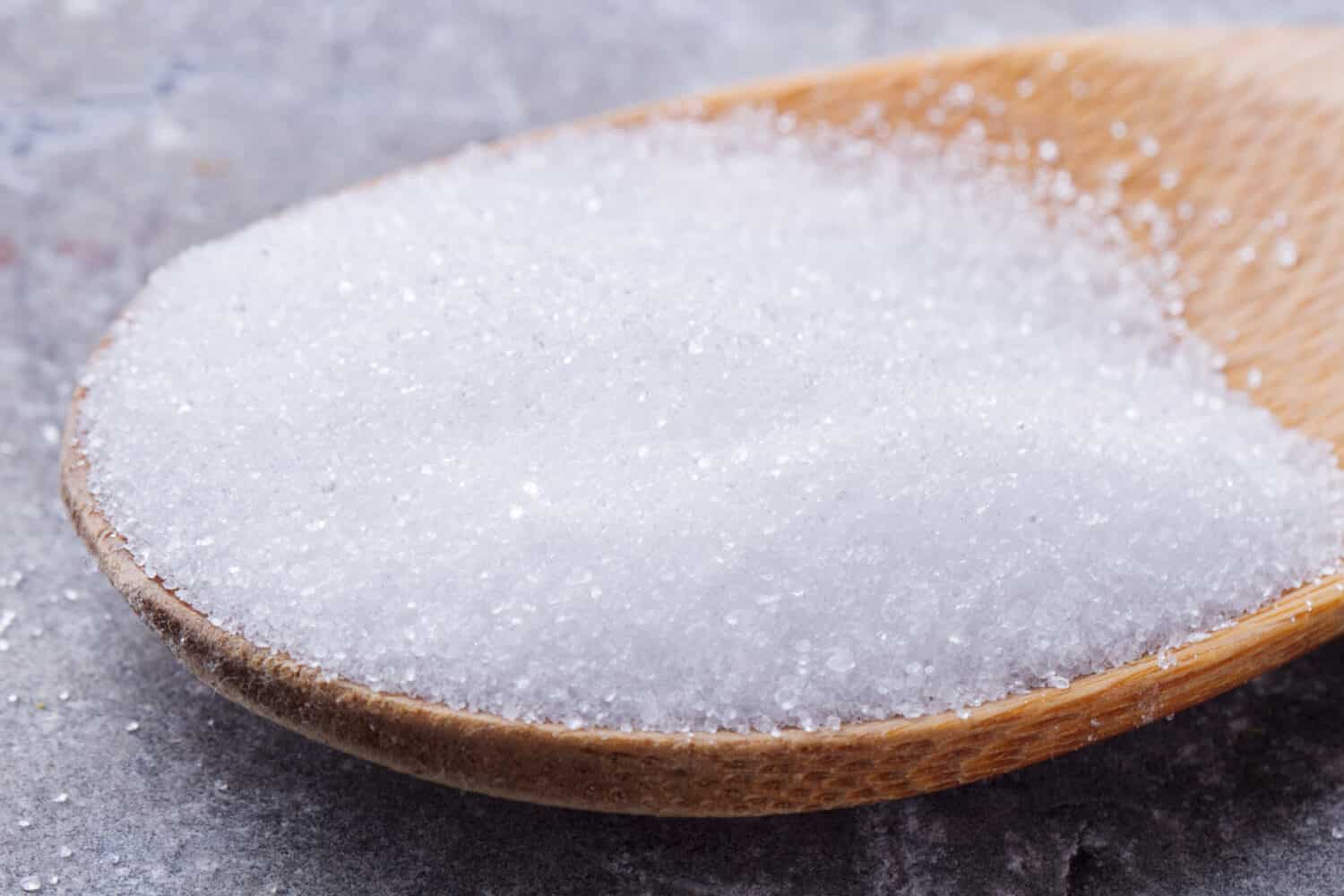
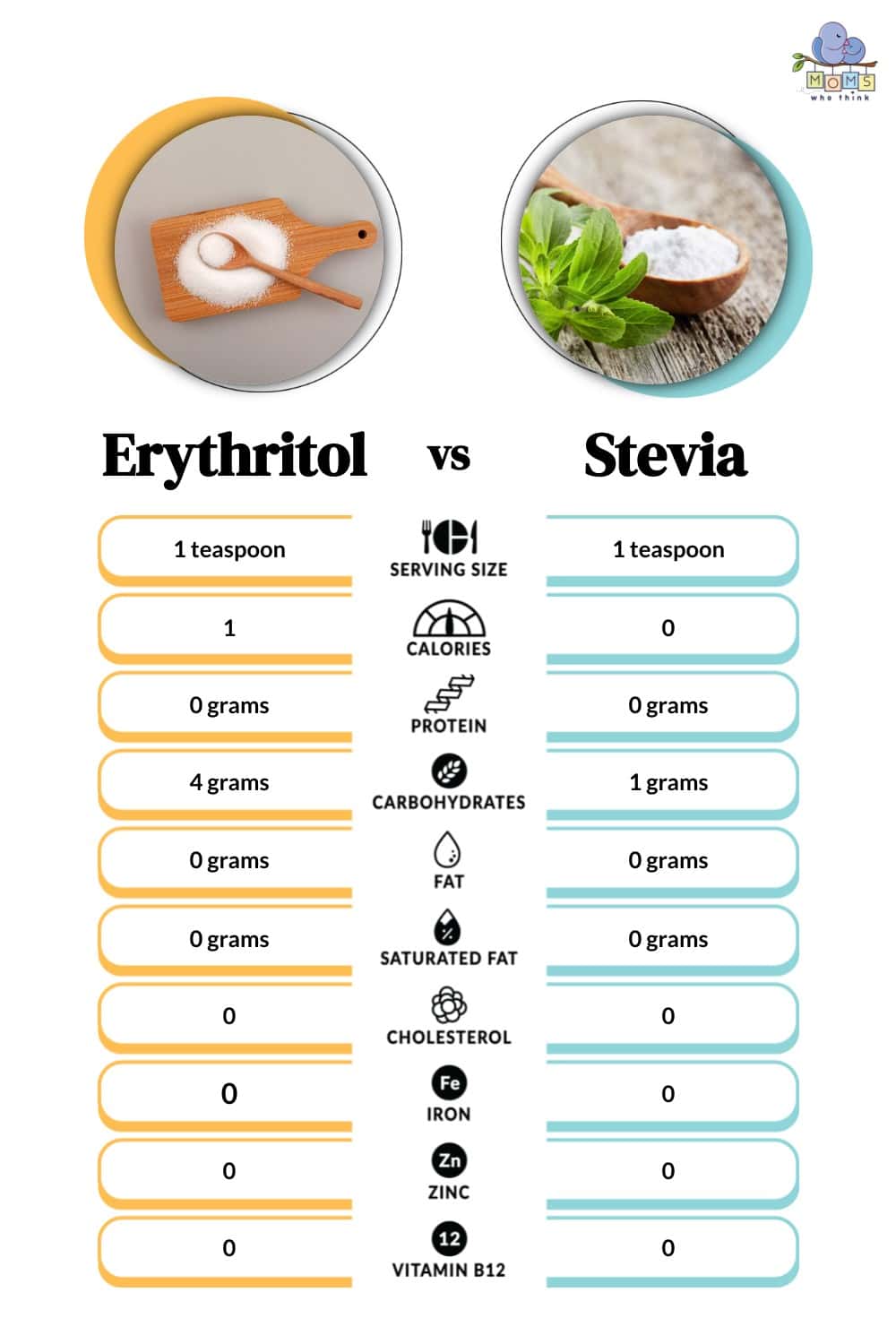
Erythritol is formed through a commercial process of breaking down, fermenting, and filtering of sugar cane or corn starch. It is an ongoing debate over whether or not can be considered a natural sugar due to its process. Erythritol is 70% sweeter than white sugar. Most people will say erythritol tastes close to sugar – without the calories. And it doesn’t have a lingering aftertaste as other natural alternative sweeteners.
Stevia, however, is a leafy herb – a natural sweetener – that comes from the stevia plant. South American natives have been using stevia for centuries. The extract from stevia is 200-400 times sweeter than sugar.
This means you only need a little bit to sweeten your food or beverage. It has a bitter, almost metallic, licorice-like aftertaste. For some, the intense sweetness is overpowering. Of course, you can control how much stevia you want to use.
What is Erythritol?
A sugar alcohol sweetener that is often a preference for sugar-free or keto diets instead of using regular sugar. There is confusion as to whether or not it is an artificial sweetener. Why? Because it's naturally present in small quantities of foods such as in fruits and vegetables. And it is also produced within our cells during regular metabolism.
However, erythritol has also been a man-made sweetener since 1990 and is available in a granular, powder, or liquid form. It is advertised as a natural sweetener, however, it is a synthetic sweetener. Why? Because it is not naturally present in corn – where it's usually made from.
A Few Things to Note On Erythritol
When you consume erythritol, your body rapidly absorbs about 10% in the small intestine and bloodstream, while the remaining 90% is excreted through urine, essentially without undergoing metabolism.
And while you can find non-GMO* options, a significant portion of the erythritol found in today's foods and drinks actually comes from cornstarch sourced from genetically modified corn.
* Non-GMO stands for “non-genetically modified organism.” It refers to foods, ingredients, or products that have not been genetically engineered or altered in a laboratory. Non-GMO foods come from plants or animals that have been grown or raised using traditional breeding methods, without the introduction of genes from other species.
What is Stevia?

©Dionisvera/Shutterstock.com
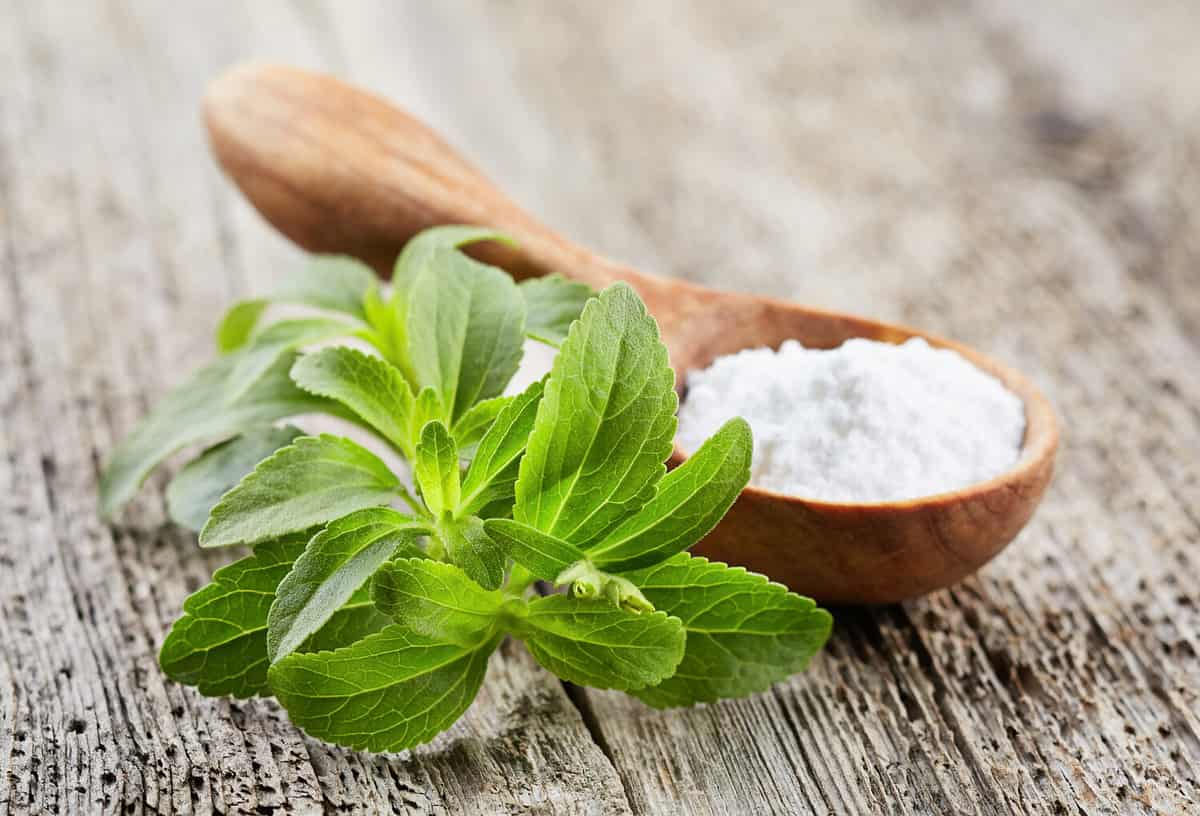
Stevia is a natural sweetener made from the leaves of a plant called Stevia rebaudiana, found in South America. It contains special compounds called steviol glycosides that make it sweet. These compounds are taken from the leaves and made into stevia sweeteners. Unlike artificial sweeteners, stevia comes from a plant and is used as a natural alternative to sugar. It has no calories, won't raise your blood sugar levels much, and is kind to your teeth.
Common Uses for Erythritol and Stevia
Beverages: Often used to sweeten beverages such as soft drinks, flavored water, sports drinks, and powdered drink mixes.
Baking and Cooking: This includes cakes, cookies, bread, sauces, and marinades. It can handle high temperatures.
Desserts: Sucralose can be used to sweeten desserts like pies, cheesecakes, custards, and mousse.
Packaged Foods: Artificial sweeteners can be found in various packaged foods, such as sugar-free snacks, candies, and desserts. Make sure you read the labels.
Low-Calorie and Sugar-Free Products: This is a popular ingredient in low-calorie or sugar-free products, including diet sodas, ice creams, yogurts, and protein bars.
And here’s some good news: Both erythritol and stevia are heat stable. That means they can withstand high temperatures without losing their sweetness or undergoing significant chemical changes. This makes both of them suitable for cooking and baking applications.
Erythritol vs. Stevia: Pros and Cons
If you’ve got a sweet tooth – you’re certainlty not alone! The average American consumes well over 20 teaspoons of added sugar on a daily basis, which adds up to an average of 142 pounds of sugar per person per year! That’s more than two times what the USDA recommends and is proof of sugar’s addictive nature. Both erythritol and stevia are some of America’s favorite sugar substitutes.
Erythritol
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, erythritol is a safe alternative to sugar. Yet as with many sugar alcohols, they can lead to digestive problems. For example, consuming too much of this sweetener can result in discomfort such as gas, making you feel bloated, and even causing diarrhea. Also there are ongoing studies that are raising a concern over the connection between erythritol and cardiovascular problems.

©Dina Photo Stories/Shutterstock.com
Keep in mind erythritol is naturally found in fruits such as grapes, watermelon and pears. So naturally occurring erythritol isn’t the problem. It’s the high doses of erythritol – manufactured as an artificial sweetener – found in packaged foods that can wreak havoc on your body. And you can find it just about everywhere in grocery stores and restaurants, from soft drinks to “diet” foods. However, little is known about the long-term health effects.
At the same time, there is ongoing research to show that erythritol in small amounts can be safe. Why? Because it's rapidly absorbed in the small intestine but poorly metabolized. But to prevent potential side effects, adults should limit their daily intake if taking erythritol.
And here’s something surprising you may not have known about erythritol: The National Institutes for Health published a report from the journal Nutrients on an in-depth review of this sweetener and the effects it has on your teeth.
Turns out, erythritol is tooth-friendly because it does not promote tooth decay. It's been proven to effectively reduce cavity formation and keep mouth bacteria growth in check. That may be why a lot of sugar-free gum and oral care products include it as one of their key ingredients. Now that’s great news!
Stevia
Stevia is known for being a healthy, natural plant-based sweetener. It's great for people who need to manage their sugar levels. Why? Because it doesn’t impact blood sugar. And there are over 200 studies that show stevia as a safe alternative to regular sweeteners. It is also gentler than refined white sugars, easier on the body’s blood sugar, and available in most stores across the United States.
One thing to note – while rare – a few people could be allergic to stevia. So look out for signs like hives or breathing issues.
So all in all, whether you choose erythritol or stevia – you can see from the information above that there are many key factors to consider. And while both erythritol and stevia won't affect blood sugar, please keep in mind they are not a substitute for diabetes treatment.
Erythritol vs. Stevia: Which is Healthier?
As with any sweetener, moderation is the key. So while it’s a great way to cut down on sugar and still satisfy that sweet tooth – here’s what you can keep in mind: Both erythritol and stevia, are popular sugar substitutes with distinct characteristics. Erythritol, derived from corn through fermentation, offers a sugar-like taste without impacting blood sugar levels, but overconsumption might lead to digestive issues like gas and diarrhea. However keep in mind it is a man-made artificial sweetener that can impact your health in a negative way. Research is ongoing in this area.
On the other hand, stevia, a truly natural leafy herb that’s intensely sweet, has no calories, and doesn't raise blood sugar. But some find its taste slightly bitter, even licorice-like. Choosing between the two depends on personal taste preferences and sensitivities. So now you can make an informed choice. And if needed, consult with a healthcare professional so you can enjoy those sweet moments!
More Comparisons
Maple Syrup vs. Artificial Sweeteners